Complete
Works to kill the root of the infection and relieve symptoms

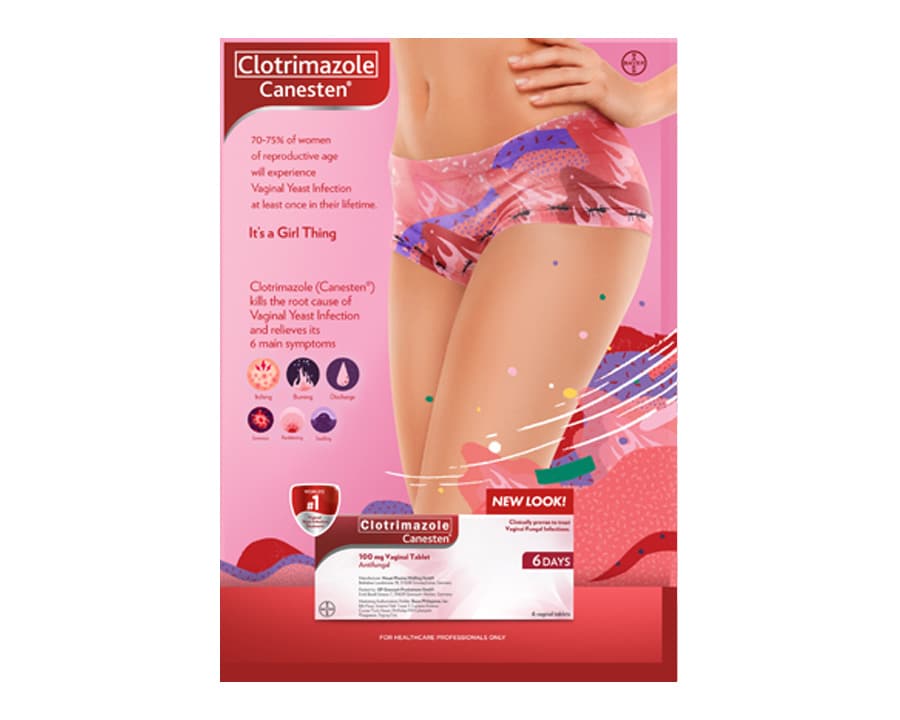
6 main symptoms:
Wash your hands thoroughly before and after using Clotrimazole (Canesten®)
Unless otherwise prescribed by the doctor, the vaginal tablet should be inserted as deeply as possible into the vagina in the evening before going to bed. Insertion is best achieved when lying back with the legs slightly drawn up.
Clotrimazole vaginal tablets need moisture in the vagina to dissolve completely, otherwise undissolved pieces of the vaginal tablet might crumble out of the vagina. To prevent this, it is important to insert the medication as deeply as possible into the vagina at bedtime. Should the vaginal tablet not dissolve completely within one night, the use of vaginal cream should be considered.
For treatment of vaginal infections use Clotrimazole (Canesten®) 100 mg Vaginal Tablet 6-day Treatment: 1 vaginal tablet to be introduced each evening on 6 successive days. Intended for use by adults and children 12 years of age and older.
Note: Pregnant women should strictly follow the instruction of their doctor.
Vaginal yeast infection is a disease characterized by signs, symptoms of vaginitis, vaginitis and presence of fungi (mainly Candida). This is the second most common cause of vaginitis, and up to 75% of women of reproductive age have at least one vaginal yeast infection, [1,2] about 40-45% of patients will have the recurrent condition several times and 5-8% will develop recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (up to 10%) - defined as inflammation at least four times a year. [3,4]
Symptoms of vaginal yeast infection include itching, burning, discharge, soreness, reddening, swelling.
References:
Candida albicans is the main causative agent of vaginal yeast infection, accounting for 80-92% of cases. The rest are other yeasts, mostly C. glabrata. These fungi are part of the vaginal microenvironment without causing symptoms in about 20% of healthy women. [1]
Classification of vaginal yeast infection: uncomplicated and complicated. Uncomplicated VYI occurs at a low frequency (<4 times per year), with mild to moderate symptoms, most likely caused by Candida albicans, and the infected women have a normal immune system. Complicated VYI is characterizd by one of the following: persistent inflammation (4 or more times per year), severe vaginitis, non-Candida albicans or co-morbidities such as diabetes mellitus, immunosupression, use of immunosuppressive drugs. [2]
References:
Vaginal yeast infections occur mainly in women of reproductive age, with epidemiological data showing that at age 25, about 50% of women had at least one vaginal yeast infection. [1] Vaginal yeast infections are very rare in preteen girls, with rates beginning to increase at age 20 and reach the peak in the 30 to 40 age group. The rate of vaginal yeast infections is linked to the amount of estrogen in the body, as increased estrogen levels increase glycogen levels in vaginal tissues, creating a carbon source for Candida. This explains why vaginal yeast infections mainly occur at reproductive age. [2-4]
References:
Vaginitis caused by Candidasis usually develops at the end of the ovulation cycle (within about a week before the start of the new menstrual cycle).[1,2] Vaginal yeast infections occur at this stage possibly due to the hormonal imbalance leading to reduced cell-mediated immune response.[1,2,3]
References:
ASC Reference No.:
B0011P011124C, B0058P011524C, B0060P011524C, B0061P011524C, B0062P011524C, B0063P011624C, B0048P012324C, B0053P012324C, B0054P012324C, B0179P012324C